What is QMI?Main Features
Figure 1

Montage of QMI drivers manufacturer and
devices
Figure 2
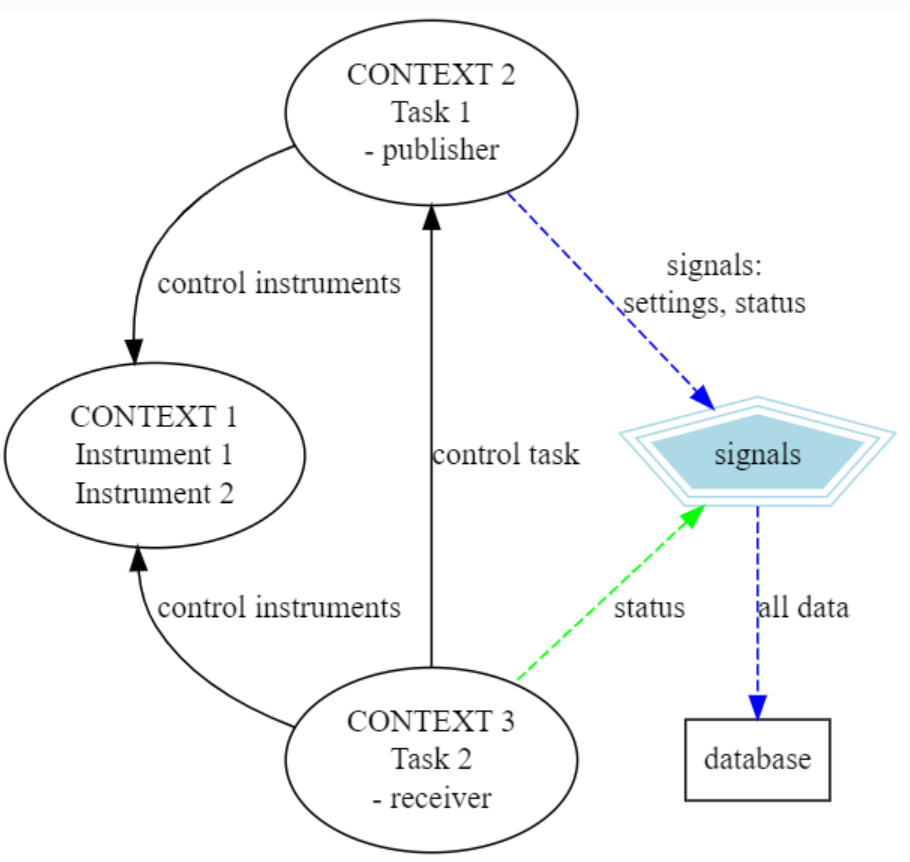
Figure 1: An example of three QMI contexts where
two instrument device drivers are added to QMI context 1. Then we have
context 2, that runs a task, which is configured to make connection to
context one, and to control the instruments in it. This second contexts
now sends also out settings and status signals which can e.g. be
forwarder to a database. A third context monitors the task status in
context two and instrument status in context one. This context is hooked
in the status signal and at specific signal values or circumstances
could either tell context two to change settings or stop task, or send
specific commands to the instruments in context one.
'Hello World'
Controlling an instrument
Configuring and logging
Accessing an instrument remotely
Create a task and a 'service'
Open-source vs internal code
Figure 1
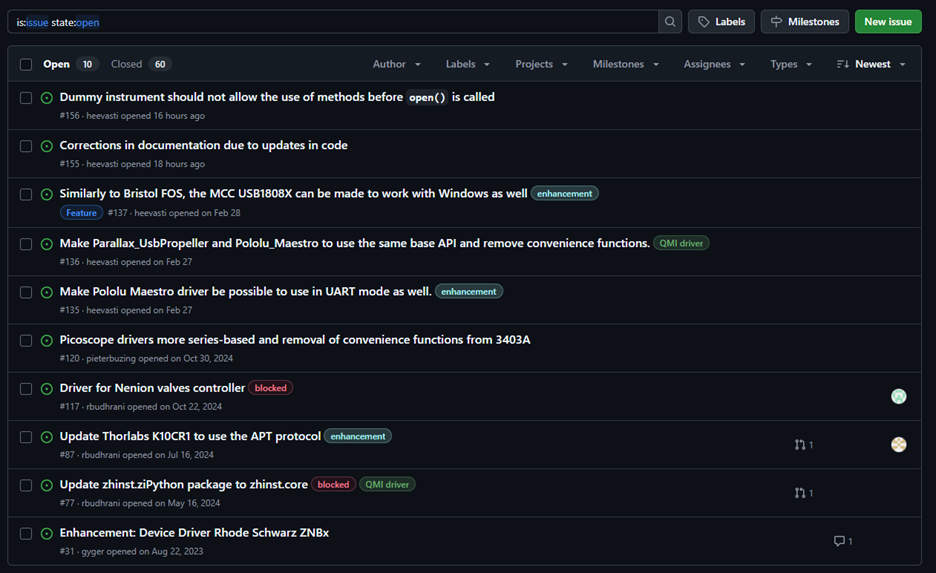
Figure 2: An issue list in Github.
Figure 2
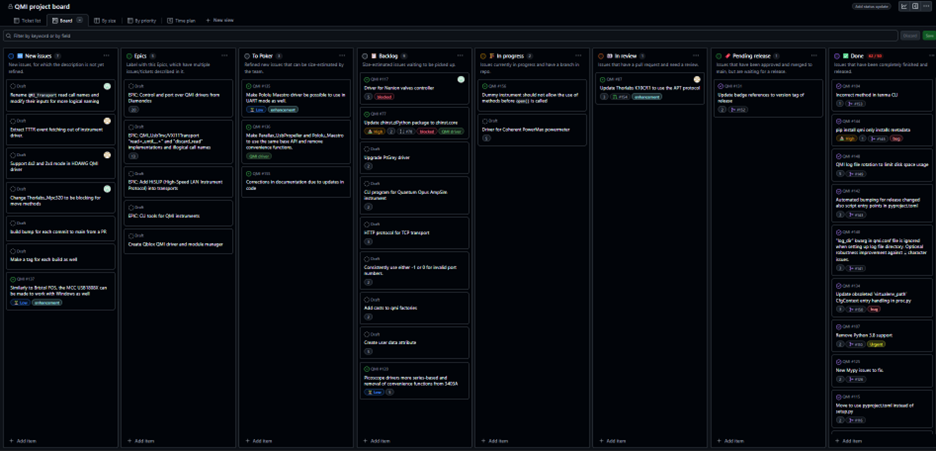
Figure 3: QMI issue development board.
